Introduction to Chem:
—-----------------------------------
The Difference between mass and volume:
There are three different types of matter and how the particles move determines the state
of matter.
Gas:
Liquid:
Solid:
…………………………………………………………………………
Mass:
Mass is the amount of force gravity has on an object.
Volume:
Volume is the amount of space the object takes up.
The three states of matter:
1, Solid
2, Liquid
3, Gass
Solids
Ice
Table
Rock
Liquids
Water
Blood
Oil
Gases
Neon
Carbon Dioxide
Helium
Defusion:
Part of the theory
One way we can observe how the particles move
It's the gradual way that the particles move/mix together
—-------------------------------------------
Experiment 1-Diffusion:
…………………………………………
Method:
We took two petri dishes and filled one with hot water and the other with cold water.
We then used a spatula to put a pinch of Potassium Permanganate in each of them.
Observations:
The Potassium Permanganate turned purple in the water. The hot water had cooled down
before we put the Potassium Permanganate in so it spread at the same rate as the cold
water.
Should have happened:
The hot water dish should have spread a lot further and faster than the cold water dish
because of the high concentration gradients in the hot water compared to the low
concentration in the cold water.
Experiment 2-Revisiting defusion:
…………………………………………………………………
Aim:
The aim was to get the hot water patriot dish to defuse a lot further and faster.
Method:
We took two petri dishes and filled one with boiling water and the other with cold water.
We then used a spatula to put a pinch of Potassium Permanganate in each of them.
Observations:
The Potassium Permanganate turned purple in the water. The hot water had cooled down
before we put the Potassium Permanganate in so it spread at the same rate as the cold water.
Mrs Bedford also put more Potassium Permanganate in the cold water and just a small amount
in the hot water. So our cold water petri dish spread further.
Explanation:
The hot water dish should have spread a lot further and faster than the cold water dish
because diffusion speeds up in heat.
Different bases:
..................
Milk:
The milk petri dish did defuse but at a very slow rate and underneath not on top because
it is more vissics than water. The Potassium Permanganate also went brown because there
are a lot of other sugars and it is more viscous than water. It sank to the bottom because
of the high surface tension and KMn04 is heavier than the milk.
Canola Oil:
The Canola oil petri dish did not diffuse at all; it just sat on top of the oil because of
the high amount of viscous in the oil.
Essential Oil:
The essential oil did not spread either because of the high amount of viscous in the oil
but if we heated the oil up iit would have defused because oil gets thinner as it heats up.
Questions From Diffusion Video:
1.Diffusion is when the smell of something mixes with air molecules.
2.The molecules move by mixing in with the air molecules so they can then spread out with
the wind and air.
3.You can speed up diffusion by using heat and you can slow it down by cooling it down.
4.Some examples of diffusion are coffee, tea and hairspray.
Ice melting:
.............
Method:
We placed ice in glass bowls, plastic petri dishes and in a cold aluminium tray.
Observations:
The aluminium tray melted the ice quicker because of the energy transferred from the room
temperature air (21 Degrees) & the aluminium tray combined with the larger surface area
than the bowl or the dish this made the ice melt faster. The plastic and glass also don't
transfer energy as fast as the aluminium tray/cant conduct heat..
Ice Melting 2, With bunsen burner:
……………………………………………………………………………………
Observations:
In the beginning the ice measured in at 5 degrees but as it started to melt it heated up
very quickly. After about 10-15 minutes it was at 22*.
This is a table of our results.
Time (min)
|
Temp
|
Time (min)
|
Temp
|
Time (min)
|
Temp
|
3
|
30*
|
6
|
62*
|
9
|
96*
|
4
|
35*
|
7
|
70*
|
10
|
103*
|
5
|
52*
|
8
|
87*
|
11
|
104*
|
Substances:
.............
Different substances have different properties.Pure substances only contain one
substance while a mixture contains as many as you want. Most of the materials around us are
mixtures not very many pure substances exist.
Examples:
Coffee, tea, fizzy drinks, hair gel, condiments,
Properties:
Properties are how we identify substances.
Questions:
1. The features by which material can be identified are called properties.
2. Materials which always have the same properties are called pure substances.
3. Materials which are made up of different substances are called mixtures.
4. Orange juice is a mixture not a substance because in the juice there are many different
substances such as, sugar, Vitim C/ abscorbic acid, citric acid, juice, sweetener, water,
hydrogen, and orange pulp.
Solutions:
When you stir sugar into water it seems to disappear. We say it has dissolved into
the water. Sugar and water have mixed to form a solution Coffee and water also form
a solution. When you dissolve coffee in hot water the substance that dissolves
(the coffee) is called a Solute. The substance that does the dissolving (the hot water)
is called the solvent.
Suspension:
A suspension is when a salute is suspended in a solvent. it doesn't dissolve it just sits
there.
E.g: Snow in a snow globe.
Experimenter #3 Imploding.
Cans.
When we put the can with 50 m of water in it onto the Bunsen Burner it took about 7 minutes
to start steaming.We then put it upside down in cold water as soon as the can opening was
submerged it imploded suddenly.
Ball & Ring.
Mrs Bennett heated up a brass ring over the Bunsen Burner so that when the ring expanded
due to thermal heat it could fit over the brass ball. But as soon as she submerged the
ring in cold water it could no longer fit over the brass ball.
Dropping Pins Experiment:
Aim:
The aim of this experiment was to watch conduction as the heat transferred down the metal rod dropping
the pins as the glue heated up and melted.
Equipment:
We used a Bunsen Burner and the equipment that came with it,retort stand,6 pins,petroleum jelly and a
metal rod.
Method:
First we glued the pins at even intervals along the metal rod with petroleum jelly, then we set up the
bunsen burner with the retort stand beside it with the metal rod attached to it.
Result:
The pins dropped as the heat transferred along the metal rod therefore melting the jelly that stuck the
pins on causing them to drop.
Conclusion:
Because of the conduction of thermal energy transferring down the rod the thermal energy melted the
petroleum jelly jelly releasing the pins causing them to fall off the metal rod.
Tea Bag Rocket
What happened was pretty much what me and Liv were expecting once the tea bag had been lit on fire it
launched its self up into the air as carbon and ash before floating back down. This happens because of
the change in the air density inside the tea bag is different to the air density from out side the tea
bag.This is because the cold air rushes into the tea bag pushing it up into the air.
Chromatography
Chroma is greek for colour Graphy means words or pitchers.
Chromatography is the scientific technique for seperating 2 or more coloured pigments(inks & dyes).
Questions:
1) Chroma is greek for colour and Graphy means words or pitchers in greek.
2) Inks and dyes
3) The pigments seperate because
4) Lighter pigments are carrieded further than darker pigments in a solvent.
5) The "start line" should always be drawn in pencil because pencil is graphite which doesn't seperate.
6) The solvent level must be lower than the sample spots because
Saturation
A saturated solution is when no more solvent can be dissolved in it. If some of the solvent evaporates from a
saturated solution, the remaining solution becomes supersaturated. The remaining solute will then begin to form
crystals.
Epsen Salt Crystals
When we were making our crystals we tried to saturate water with epsen salts but we couldn't get the liquid
saturated. Because of this crystals grew in the solution but coudn't hold their form in tthe liquid. We then
tried to grow the cyristals in the same solution but on a pipe cleaner but with no success.

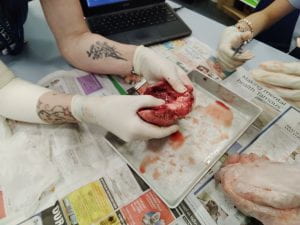
 Explanation:
At the top of the heart is the aorta. In the middle is all the heart strings that connect everything together.
Conclution:
Everything did work the way that I expected it to. The only thing that I wasn't expecting was the way it smelt
and how squishy and meat like it was.
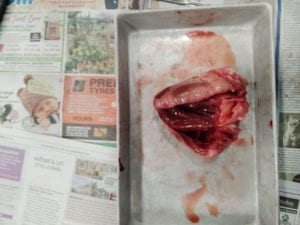
Explanation:
At the top of the heart is the aorta. In the middle is all the heart strings that connect everything together.
Conclution:
Everything did work the way that I expected it to. The only thing that I wasn't expecting was the way it smelt
and how squishy and meat like it was.

 Different States Of Matter:
Different States Of Matter: